A) large globular clusters
B) Planets in our own Solar System
C) Supernovae
D) Cepheid variable stars
E) Wrong.All of these could be used
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When two galaxies collide,they pass through each other,and their stars almost never collide.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dark matter in galaxies has been hypothesized to be composed of
A) neutral hydrogen clouds.
B) dust particles.
C) weakly interacting massive particles.
D) H II regions of glowing hydorgen gas.
E) all of the above
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the primary factor in determining the classification for an elliptical galaxy?
A) Size
B) Shape
C) Mass
D) Color
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tuning fork diagram is shown below.Which of the labeled figures represents an Sa galaxy? 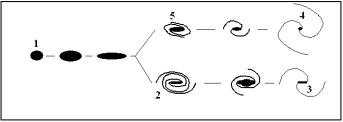
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Astronomers now speculate that a galaxy's shape depends on all of the following EXCEPT
A) the rate of star formation.
B) the history of past collisions.
C) the mass.
D) its direction in the sky as seen from Earth
E) All of the above are important in determining a galaxy's shape.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We should expect galaxies to collide with each other fairly often because
A) a galaxy's size is comparable to (but smaller than) the average distance between galaxies.
B) galaxies contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen.
C) galaxies occur in clusters.
D) a and c
E) none of the above
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The units on the Hubble constant are ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If H equals 50 km/sec/Mpc,then a galaxy with a radial velocity of 50,000 km/sec will have a distance of about 1 Mpc.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the mass of a galaxy is contained in the
A) massive O and B stars in the galaxy.
B) neutral hydrogen gas H I regions of the galaxy.
C) ionized hydrogen gas H II regions of the galaxy.
D) dark matter halo of the galaxy.
E) disk ofstars in the galaxy.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rotation curve of a galaxy (orbital speed versus distance) can be used to determine
A) the colors of hot young stars in the galaxy.
B) the elements which make up the galaxy.
C) the direction in the sky of the galaxy.
D) the age of the galaxy.
E) the mass of the galaxy.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What distance method did Edwin Hubble use to determine the distance to local galaxies?
A) Hubble Law
B) Supernova observations
C) Period-luminosity relationship of variable stars
D) Parallax
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An E galaxy contains
A) mostly lower-main sequence stars and giants.
B) mostly upper main sequence stars and giants.
C) mostly upper main sequence stars and gas and dust.
D) roughly equal numbers of upper and lower main sequence stars.
E) mostly white dwarfs and supergiants.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An irregular galaxy contains
A) mostly lower-main sequence stars and giants.
B) mostly upper main sequence stars and giants.
C) mostly upper main sequence stars and gas and dust.
D) upper and lower main sequence stars and gas and dust.
E) mostly white dwarfs and supergiants.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Elliptical galaxies are primarily made up of massive O and B stars.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a large galaxy collides with a small galaxy,the smaller galaxy may be pulled apart by tidal forces.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An elliptical galaxy could
A) evolve into an irregular galaxy when it has used up all of its gas and dust.
B) be formed from the collision and merger of spiral galaxies.
C) evolve from a single spiral galaxy when the spiral has used up all of its gas and dust.
D) become a solar system some day.
E) be at the center of our Solar System
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most massive galaxies are
A) spiral galaxies.
B) giant elliptical galaxies.
C) dwarf elliptical galaxies.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
____________________ clusters of galaxies contain closely spaced galaxies and often contain giant elliptical galaxies and a hot intergalactic medium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
____________________ galaxies have a definite disk component but contain no evidence of spiral pattern,few hot young stars,and little gas and dust.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 55
Related Exams