A) tripod
B) blow-out
C) Le Fort
D) contrecoup
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Part 3 is part of which bone? 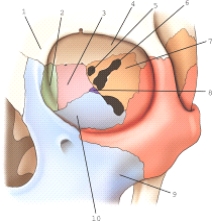
A) Palatine
B) Sphenoid
C) Lacrimal
D) Ethmoid
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The posterior aspect of the orbit is termed the:
A) apex.
B) base.
C) sphenoid strut.
D) crown.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which positioning line is parallel to the IR for the oblique inferosuperior (tangential) projection of the zygomatic arches?
A) Midsagittal plane
B) Infraorbitomeatal
C) Orbitomeatal
D) Glabelloalveolar
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What can the technologist do if the patient cannot extend the head and neck adequately for the routine submentovertical projection of the zygomatic arches?
A) Perform the Haas method.
B) Use a short SID to magnify the arches.
C) Angle the CR to place it perpendicular to the IOML.
D) Rotate the skull 15° away from the affected side.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is the CR centered for a lateral projection of the facial bones?
A) Outer canthus
B) Acanthion
C) Midway between the glabella and the EAM
D) Zygoma, midway between the EAM and the outer canthus
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match each of the following radiographic appearances with the corresponding pathologic indication.(Use each selection only once.) -Distinctive lesions with moth-eaten appearance, a combination of increased density and destructive irregular border lesions
A) Multiple myeloma
B) Paget's disease
C) Metastases
D) Pituitary adenoma
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The lateral projection of the facial bones is typically a unilateral projection.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where are the ethmoid sinuses located within the ethmoid bone?
A) Perpendicular plate
B) Pterygoid processes
C) Cribriform plate
D) Lateral masses
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An average-shaped skull with a 47° angle between the petrous pyramids and the midsagittal plane is classified as:
A) mesocephalic.
B) brachycephalic.
C) dolichocephalic.
D) morphocephalic.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match each of the following radiographic appearances with the corresponding pathologic indication.(Use each selection only once.) -Radiolucent areas within the bony cranium
A) Multiple myeloma
B) Paget's disease
C) Metastases
D) Pituitary adenoma
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient enters the ED with facial bone injuries.The physician is concerned about a possible blow-out fracture of the left orbit.Which one of the following projections would best diagnose this injury?
A) Parietoacanthial (Waters method) projection
B) Submentovertical projection
C) Superoinferior (tangential) projection
D) Modified parietoacanthial (modified Waters) projection
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which bony landmark represents the highest level of the facial bone mass?
A) Nasion
B) Acanthion
C) Orbital plates
D) Supraorbital notch
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which bony structure is labeled v?  (Anatomic structures are labeled i through vi and sutures a through h.)
(Anatomic structures are labeled i through vi and sutures a through h.)
A) EAM
B) Mastoid process
C) Styloid process
D) Zygomatic process
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The recommended digital systems kV range for the superoinferior tangential (axial) projection of the nasal bones is:
A) 40 to 50.
B) 50 to 60.
C) 70 to 80.
D) 75 to 85.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient comes to radiology with acute mastoiditis.Which one of the following imaging modalities will best demonstrate possible bony destruction within the mastoid region?
A) CT
B) Nuclear medicine
C) Ultrasound
D) PET
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following projections will best demonstrate the entire mandible with one exposure?
A) AP axial
B) Submentovertical
C) Axiolateral oblique
D) Tomography
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cranial bone labeled i is the: 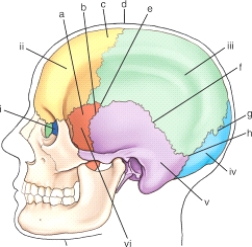 (Anatomic structures are labeled i through vi and sutures a through h.)
(Anatomic structures are labeled i through vi and sutures a through h.)
A) sphenoid.
B) lacrimal.
C) ethmoid.
D) palatine.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The modified parietoacanthial (modified Waters) projection requires more extension of the head and neck as compared with the parietoacanthial (Waters) projection.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) can provide reconstructed images in three planes: axial, sagittal, and coronal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 181
Related Exams