A) 8.
B) 9.
C) 10.
D) 11.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kara was out jogging and, despite being tired, decided to run one more mile. Based on her actions, economists would conclude that Kara
A) must be an avid runner.
B) decided that the marginal benefit of running one more mile would outweigh the cost of the additional mile.
C) decided that the marginal cost of running one more mile would outweigh the benefit of the additional mile.
D) was not very tired, so the marginal cost of the extra mile was very low.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economic analysis is primarily concerned with marginal changes from the status quo, as a result of a certain action or decision.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If price (P) and quantity (Q) are directly related, this means that
A) a change in Q will alter P, but a change in P will not alter Q.
B) if P increases, Q will decrease.
C) if P increases, Q will also increase.
D) an increase in P will cause Q to change, but the direction in which Q changes cannot be predicted.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following graph is the production possibilities curve of a nation. 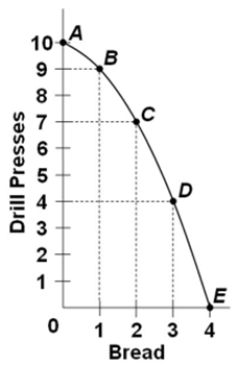 The combination "5 drill presses and 2 bread" indicates
The combination "5 drill presses and 2 bread" indicates
A) an unattainable combination for the nation.
B) that some resources in the nation are unemployed.
C) an ideal combination for the nation.
D) a combination produced when the nation is at full employment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Last Word) Which of the following has to do with the problem of distinguishing cause and effect in economic reasoning?
A) the law of large numbers
B) the law of averages
C) the post hoc, ergo propter hoc fallacy
D) the fallacy of composition
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The budget line shows
A) the amount of product X that a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one more unit of product Y.
B) all possible combinations of two goods that can be purchased, given money income and the prices of the goods.
C) the minimum amount of two goods that a consumer can purchase with a specific money income.
D) all possible combinations of two goods that yield the same level of utility to the consumer.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not be classified as an economic resource by economists?
A) a professional soccer player
B) water in a town's reservoir
C) money in a business checking account
D) the manager of the local hamburger restaurant
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The purpose of the ceteris paribus assumption used in economic analysis is to
A) avoid making normative statements.
B) distinguish macroeconomics from microeconomics.
C) make sure that all relevant factors are considered.
D) focus on the effect of a single factor on a certain variable.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a factor of production?
A) money
B) labor
C) capital
D) entrepreneur
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the price of product Y (the quantity of which is on the vertical axis) is $15 and the price of product X (the quantity of which is on the horizontal axis) is $3. Also assume that money income is $60. The absolute value of the slope of the resulting budget line is
A) 5.
B) 1/5.
C) 4.
D) 20.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Consider This) Free products offered by firms
A) may or may not be free to society but are never free to individuals.
B) may or may not be free to individuals but are never free to society.
C) are produced and distributed at no cost to society.
D) are usually items nobody wants.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nation can produce two products: tanks and autos. The table below is the nation's production possibilities schedule.  In moving from combination C to B, the opportunity cost of producing 100 more autos is
In moving from combination C to B, the opportunity cost of producing 100 more autos is
A) 2 units of tanks.
B) 1 unit of tanks.
C) 850 units of autos.
D) 1800 units of autos.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the production possibilities curve is a straight line, then
A) the opportunity cost of producing one good is zero.
B) the law of increasing opportunity costs does not apply.
C) the society can produce more of both goods simultaneously.
D) the society is capable of producing only one of the goods and not the other.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) An increase in a nation's labor supply will cause its potential output to increase.
B) Economic growth can be illustrated by an expansion of a nation's production possibilities curve.
C) An increase in the quantity of a nation's resources will cause economic growth, but an increase in the quality of resources will not.
D) New technologies or new ways of producing output can cause a nation's production possibilities curve to shift outward.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is another way of saying "marginal benefits of an action"?
A) benefits given up, once the action is taken
B) unintended gains from taking the action
C) benefits accruing to others as a result of one's action
D) extra benefits resulting from the action
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Last Word) The safest way for an individual to leave a burning theater is to run for the nearest exit; it is therefore also the best means of escape for a large audience. This assertion illustrates the
A) "after this, therefore because of this" fallacy.
B) correlation fallacy.
C) fallacy of composition.
D) fallacy of limited decisions.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One basic difference between "land" and "capital" resources is that land is
A) manufactured, while capital is created by humans.
B) unlimited, while capital is limited.
C) natural, while capital is created by humans.
D) limited, while capital is unlimited.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basic truth that underlies the study of economics is the fact that we all face
A) death.
B) taxes.
C) risk.
D) scarcity.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is operating inside its production possibilities curve for consumer goods and capital goods, it
A) can only produce more consumer goods by producing fewer capital goods.
B) can only produce more capital goods by producing fewer consumer goods.
C) can produce more of both consumer goods and capital goods by using resources that are currently idle.
D) must improve its technology to produce more output.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 398
Related Exams